

Impact
Savings: By the Numbers
Lower costs and workers’ compensation claims with Medcor’s services.
SERVICES
What We Do
-
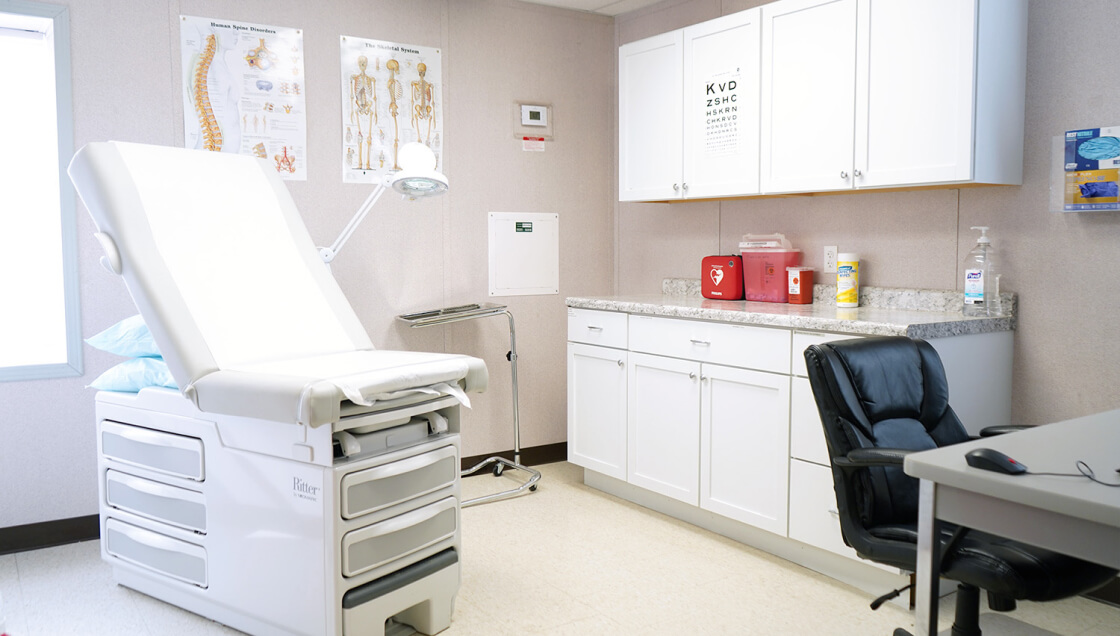
Onsite Clinics
Onsite clinics allow you to offer prompt care to ill and injured employees while decreasing your costs.Clinic Options -

Safety
Keep safety front-of-mind with tailored training and experienced professionals to staff your projects.Safety Solutions -

Telehealth
Injury triage services help with your employees’ most urgent problems.Telehealth Solutions -

Employee Wellness
Protect your investment by taking the very best care of your workforce.Explore Wellness
Insights










